Epoxy and wood glue are both adhesives you can use in the workshop. But which one should you choose for your next project? Find out here!

Epoxy, also known as epoxy resin, can adhere various materials together, including wood. Wood glue is made specifically for wood projects - it will not stick to non-wood materials very well at all!
If you're trying to choose the best type of adhesive for your next project, then read on for all the details! I'll share with you the differences between epoxy and wood glue, and some of the pros and cons to using each.
This post contains affiliate links for your convenience. Purchases made through these links may earn me a small commission at no additional cost to you. Please visit my disclosures page for more information.
Epoxy vs Wood Glue: What's the Difference?
Aside from binding materials together, epoxy and wood glue are quite different things. Let's look at each one in more detail.
Epoxy characteristics
- 5 minute epoxy is fast drying, but other types take days to cure
- It can create a strong bond between different materials
- Waterproof and weatherproof
- Fills large gaps
- Tricky to mix and use
- Has some fumes
- Can be mixed with different colors and used for crafts/tabletops/floors
Wood glue characteristics
- For use with woodworking projects only
- Slow drying
- Not as stable as cured epoxy
- Should use with clamps
- Not for large gaps
- Inexpensive (particularly regular PVA glues)
What is Epoxy?
Epoxy is a two-part adhesive that is used for many different repair tasks and DIY projects. Epoxy has many characteristics that make it uniquely suitable for tricky gluing situations.

Epoxy is fast drying (or really slow!)
For those projects where you just need to get something glued together fast, products such as 5 minute epoxy can be a great option. You just mix it together, hold the two parts in place, and within minutes you have a durable bond.
However, other forms of epoxy can take hours or days to cure! If you need a really long working time, like a complicated glue up, certain types of epoxy are a better choice than wood glue. Check the instructions to see how long it will take, and choose the right one for your project.
Epoxy is stable and durable
What does this mean? It means that epoxy can be used to fill gaps and holes in wood without losing the structural integrity of the piece. Epoxy is commonly used for creating "river tables" with live edge wood on the sides and a large gap in the center, like these gorgeous ones from BlackTail Studio.
Epoxy is waterproof
Epoxy is essentially impermeable to moisture. This makes it ideal for projects where there will be contact with moisture. If you have a project that must withstand significant weather, then epoxy is a great option. It can even be used to waterproof plywood so the layers don't separate!
When should you use epoxy instead of wood glue?
Let's talk about several times you should reach for epoxy over wood glue.
For gluing wood to non-wood material
Say you needed to permanently affix a threaded insert in a piece of wood. In this instance, wood glue would be virtually useless. However, epoxy will give you a strong hold between wood and non-wood materials such as metal.
For crafty DIY projects
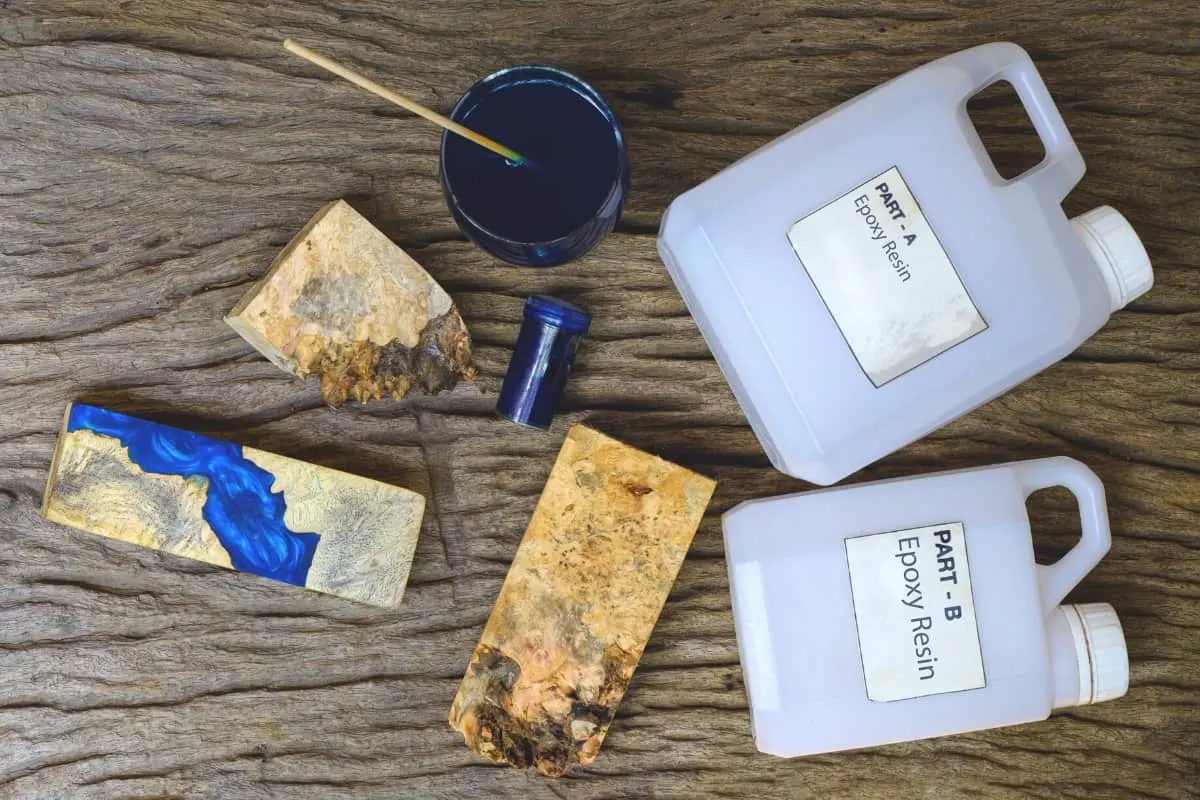
Since epoxy resin dries to a stable plastic-like material, it works great for many crafty DIY projects. You can add metallic powders, pigments and dyes to create interesting patterns and color combinations, like the ones in this video.
How Do You Use Epoxy?
Epoxies will vary in how they should be applied. Always take the time to read the fine print to make sure you're mixing it safely. With that said, here are a few guidelines.

- Safety and ventilation. Be careful when and where you use epoxy. It can emit irritating fumes. Always work in a well ventilated area. Also, it's smart to wear gloves to protect your skin.
- Clean off the surface before using epoxy. Keep the surface clean before pouring epoxy, or the dust will be trapped in the resin.
- Ensure you have everything ready to go ahead of time. Epoxy is fast drying, so make sure you have everything close at hand before you begin.
- Double check your ratios. Epoxy is a two-part substance. Usually, it's mixed two parts resin to one part hardener. If you pour too much or too little hardener, then your epoxy will either dry too fast, or it won't harden fully.
- Allow it to cure. Epoxy can get hot fast when it starts to cure, so once it's poured, don't mess with it. Some types of epoxy can cure in minutes, while others take DAYS!
What is Wood Glue?
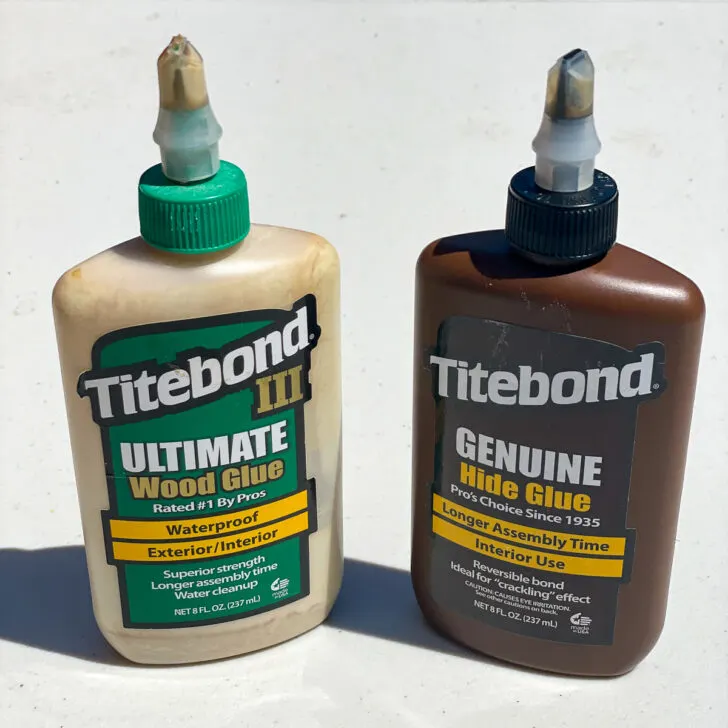
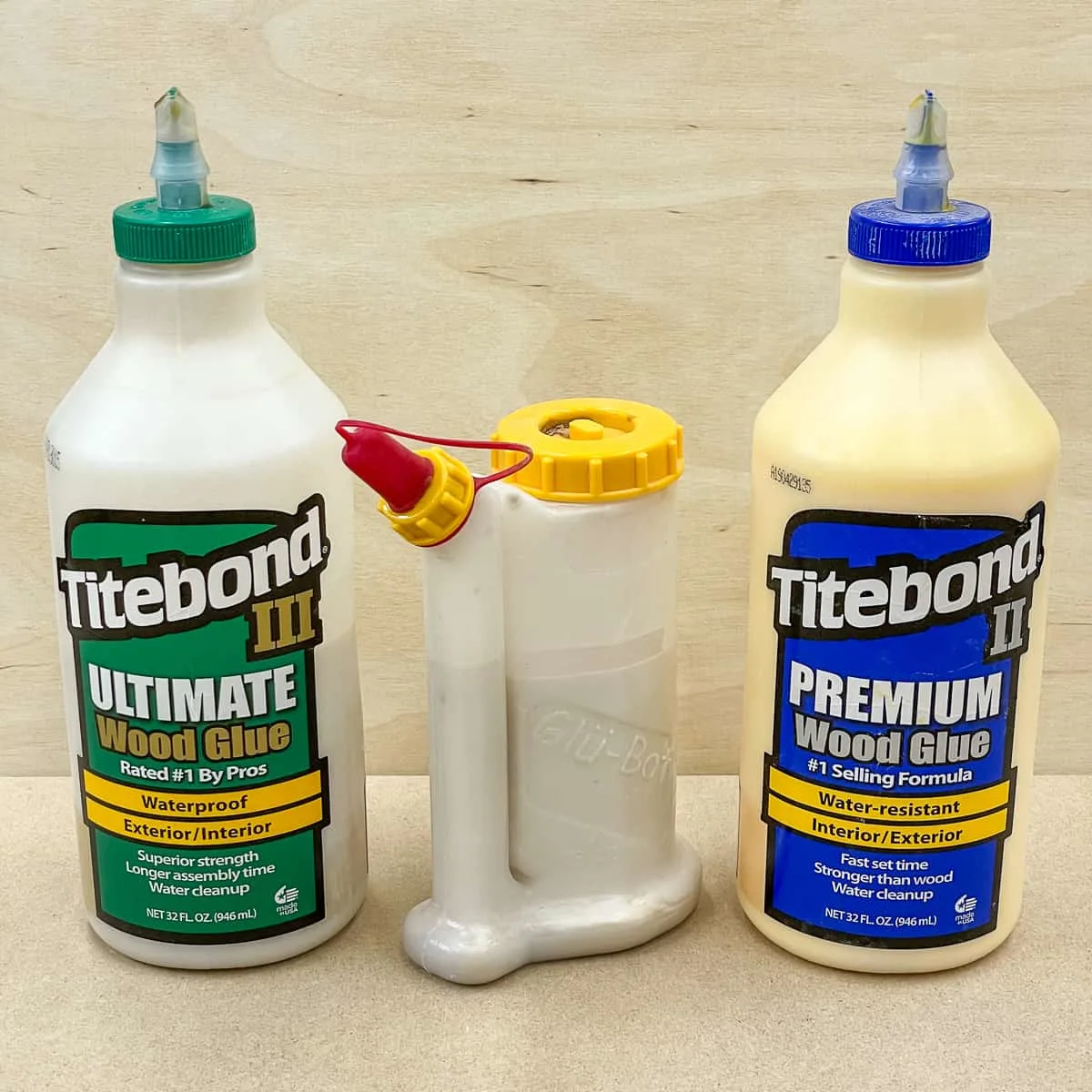
The most common type of wood glue, and the type we will focus on today, is known as PVA (polyvinyl acetate) wood glue or yellow wood glue.

Wood glue is slow drying
Compared to 5 minute epoxy, wood glue takes longer to dry. Wood glue is designed to be slow drying so that you have time to put the wood in place, secure the clamps, and make any last-minute adjustments if needed.
This is known as 'open time', and some wood glues have a longer open time than others. For example, Titebond III has an open time of about 15 minutes, while the original Titebond starts setting up in 5 minutes. If you need a longer working time, choose a two part epoxy with a slower cure time.
Once the glue starts setting up, it should stay in clamps for at least an hour to cure and bond properly. Then you can remove the clamps and continue working on your project.
Wood glue is only used for wood-on-wood adhesion
Wood glue is designed to create a stronger-than-wood connection when two boards are glued together properly. However, it will create almost no connection to other non-wood materials such as metal and plastic - this is where epoxy comes in.
With that said, some non-PVA wood glues such as CA glue (also known as super glue or Krazy glue) can form connections between wood and non-wood material.
Wood glue has very little durability on its own
Wood glue will not create a stable material by itself. For example, if you try to fill up a large knot hole with wood glue you will find that you get a goopy shrunken mess that does not accepts finishes.
When Should You Use Wood Glue?
Now that we've talked about some of the characteristics of wood glue, let's chat about some of the projects where you might use wood glue.
Between wood joints
Most woodworking projects require wood glue between the joints. Any screws or nails used can act as a clamp to hold the pieces together while the glue dries.

To repair splits
One of every woodworker's nightmares is nearly finishing a project and suddenly hearing that cracking sound. However, with some wood glue, these splits can go from disaster to minor frustration.
If you have some wood glue and some good clamps on hand, you can usually glue the wood back together and resume your project.
Bind two boards together
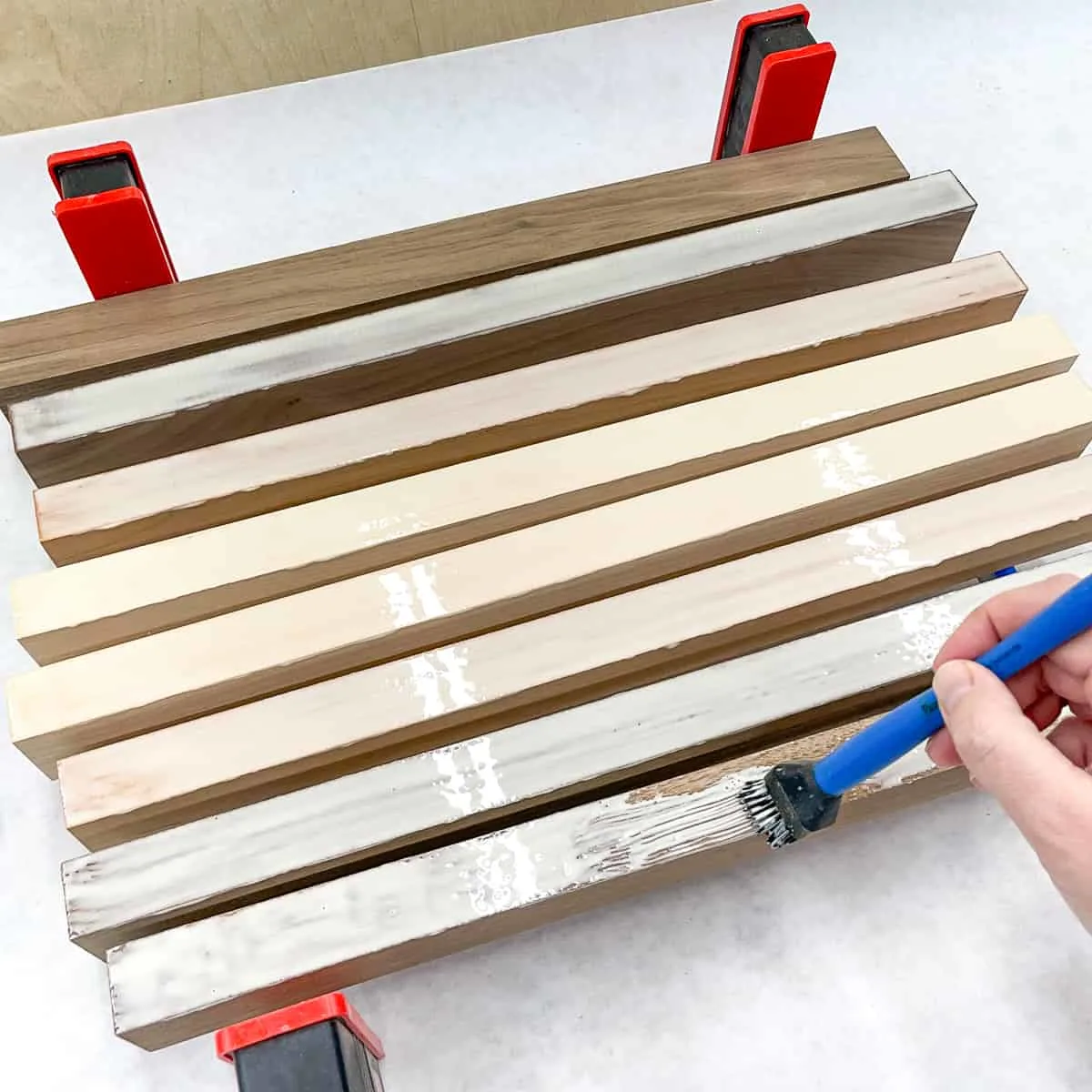
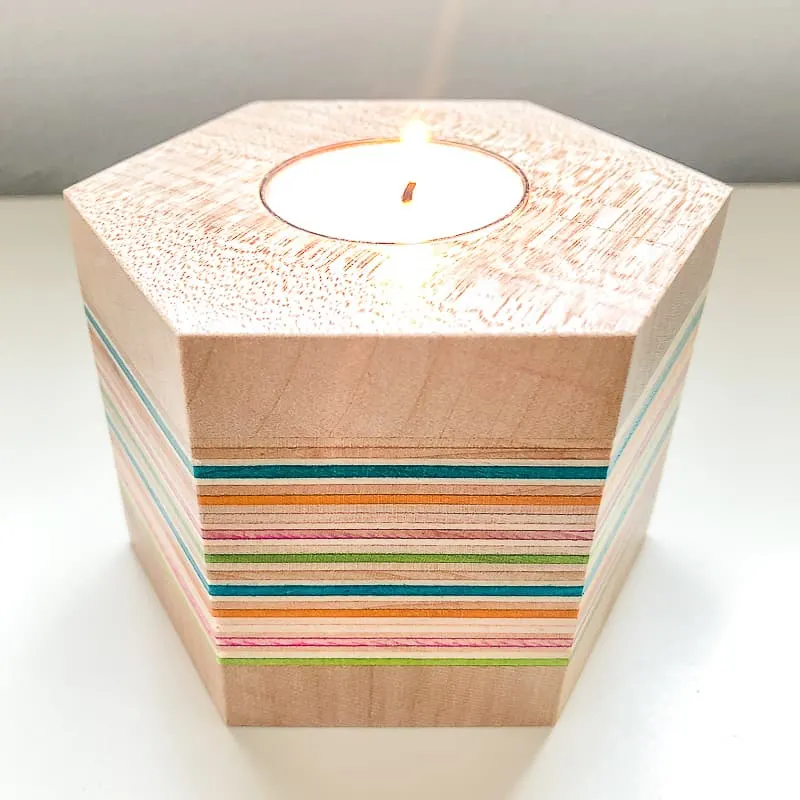
While you can't use wood glue to make a board longer, you can join the edges together to make a wider plank (like a butcherblock countertop or cutting board). You can also glue layers together like plywood to make it taller, like I did for these wood veneer candle holders.

How Do You Use Wood Glue?
Applying wood glue is fairly simple. Here are the basic steps:
- Preparation. You need to ensure that all measurements are sound, and cuts are straight before reaching for the wood glue. Unless you use something like hide glue, you cannot easily reverse a glued project once it's dry.
- Remove dust and dirt from the project. Regardless of the type of glue, it will not work well if inhibited by dust, oily substances, or old glue. Use tack cloth, a vacuum, or a microfiber rag to clean the surface before applying any glue. A clean surface will make the bond stronger.
- Beware of glue squeeze out. On some projects, it doesn't matter if the glue gets everywhere. However, sometimes glue can mess with stains and finishes, so keep a damp rag on hand to wipe up any drips.
- Use clamps. When working with traditional wood glue, clamps are a must. You need some way to hold the parts together firmly to create a strong joint.
I hope this article cleared up any confusion you might have about epoxy vs wood glue! If you have any questions, feel free to leave them in the comments below.
Check out these other woodworking articles!